AI In Robotics - New Position Paper
released by the International Federation of Robotics
“AI is transforming the field of robotics at a rapid pace," says Takayuki Ito, President of the International Federation of Robotics. “Integrating AI into robotics enhances capabilities, increases efficiency and improves adaptability. This development is transforming AI from a supporting technology into a powerful enabler, opening the door to wider robot adoption across industries.”
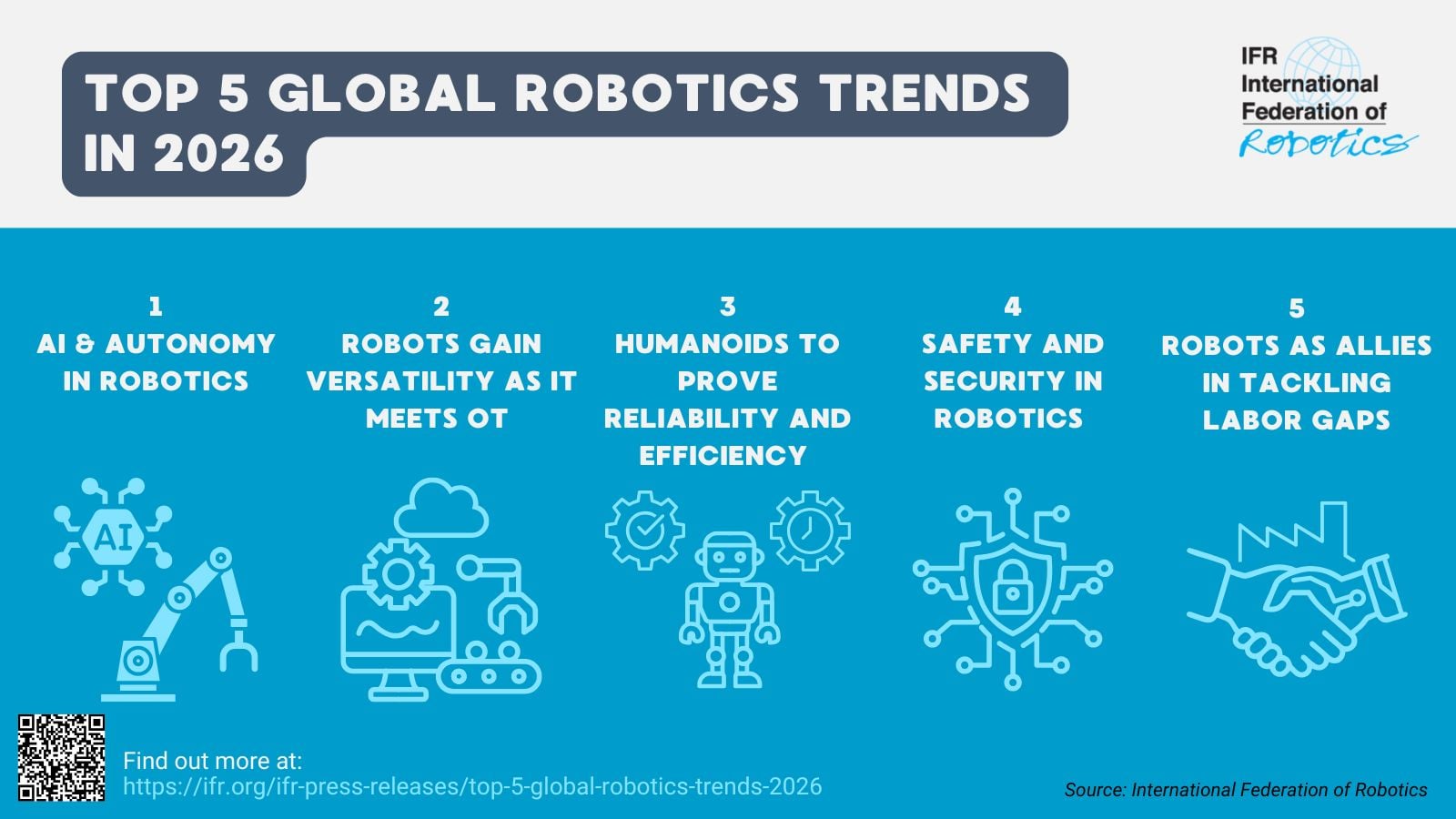
Industries at the forefront
There are currently several key sectors leading the way in integrating AI and robotics:
Logistics and warehousing are frequently cited as the leading domain. This is driven by high demand, available investment, and relatively controlled environments. Fields of adoption include logistics, warehousing and intralogistics, and the broader supply chain. The sector attracts attention for its resilience and growth potential.
The manufacturing and industrial automation sector is a focal point for investment: As companies seek to streamline operations and enhance output quality, AI and robotics are playing an increasingly central role in modern manufacturing strategies. The sector is spanning a broad array of industries. This includes automotive, electronics, and the general industries like pharma. The category encompasses high-skill production processes, factory automation systems, and precision assembly tasks.
The service sector is among the leading customers adopting AI and robotics. AI is supporting human-robot interaction, allowing for example a natural communication and increasing the usability and personalization of the robots. This trend is driven by rising costs and a shortage of workers, particularly in post-pandemic markets, where recruitment has lagged demand. Restaurants, for example, are experimenting with robotic servers and kitchen assistants. The future lies in hybrid models where robots handle repetitive tasks and humans deliver the personal touch.
New Vision for AI in Robotics
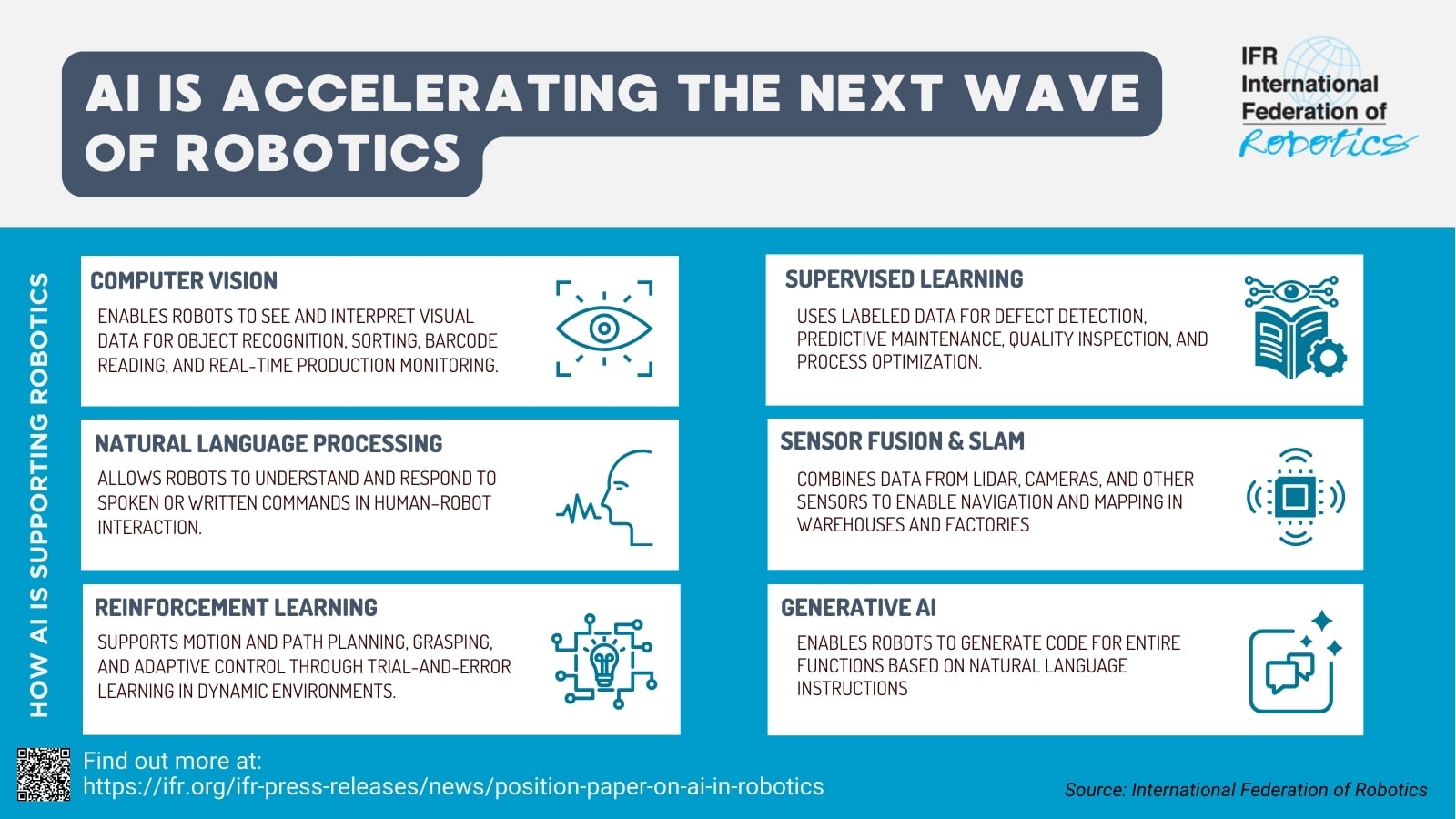
Robot and chip manufacturers recently are investing in dedicated hardware and software that simulate real-world environments. This so-called Physical AI allows robots to train themselves in virtual environments and operate by experience, rather than programming. The excitement about embodied AI has drawn attention from major tech players and governments around the world.
In the United States, companies like Amazon, Tesla, and NVIDIA have announced record-breaking investments. Venture capital is pouring into a growing ecosystem of startups focused on specialized robot applications.
In Europe, ABB announced it had signed an agreement to divest its robotics division to Japan’s SoftBank Group, combining ABB Robotics’ with SoftBank’s capabilities in AI.
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) announced a dedicated action plan to accelerate embodied AI, positioning it as “future industry” critical to China’s economic transformation.
Outlook
Over the next five to ten years, AI is expected to be widely adopted in various robotics applications. Because AI increases efficiency, reduces errors, and maintenance costs, companies often see a quicker return on investment (ROI) compared to non-AI systems.
About the “AI in Robotics” position paper by IFR
Free download at https://ifr.org/papers/downloa...
Content overview:
- How AI is supporting robotics
- Industries at the forefront
- AI is reshaping work
- Macroeconomic Trends impacting AI
- Safety and security for AI in Robotics
- Addressing Sustainability
- AI regulations by Governments
- Outlook
Contact
International Federation of Robotics
PRESS OFFICER
Carsten Heer
phone +49 (0) 40 822 44 284
E-Mail: [email protected]